AXONIUS PLATFORM
Exposures
Put your proactive cybersecurity measures in the driver's seat with a single place to unify exposure findings, correlate and rank risks, and execute prioritized large scale mitigation efforts.
Take action with exposures before they become exploits
Exposures come in many forms from all angles – vulnerable software, non-compliant devices, app misconfigurations, weak access controls, public data access, and more. Axonius helps you make sense of which risks deserve attention with continuous asset discovery, intelligent assessments, and streamlined remediation workflows.
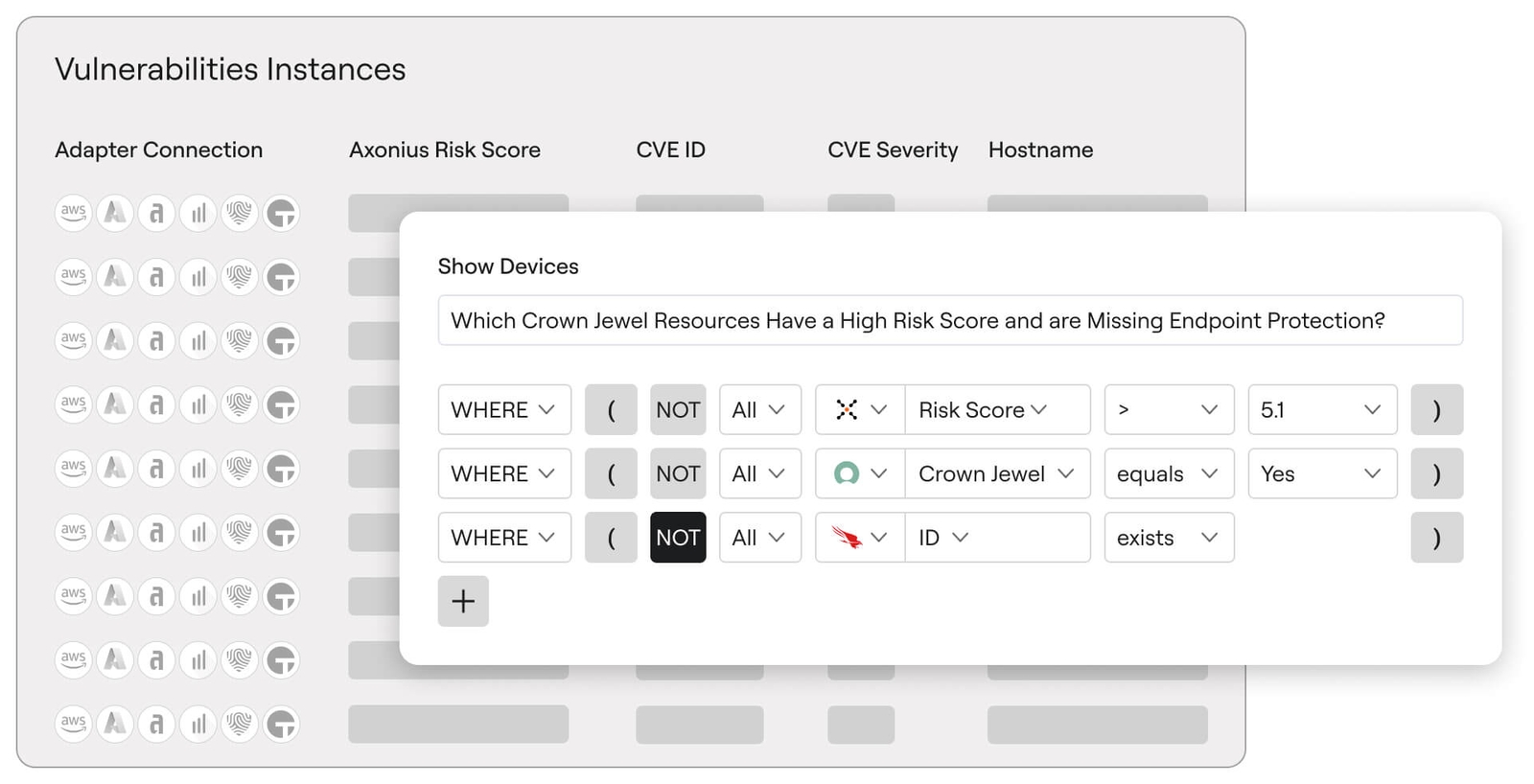
Turn fragmented findings into actionable insights
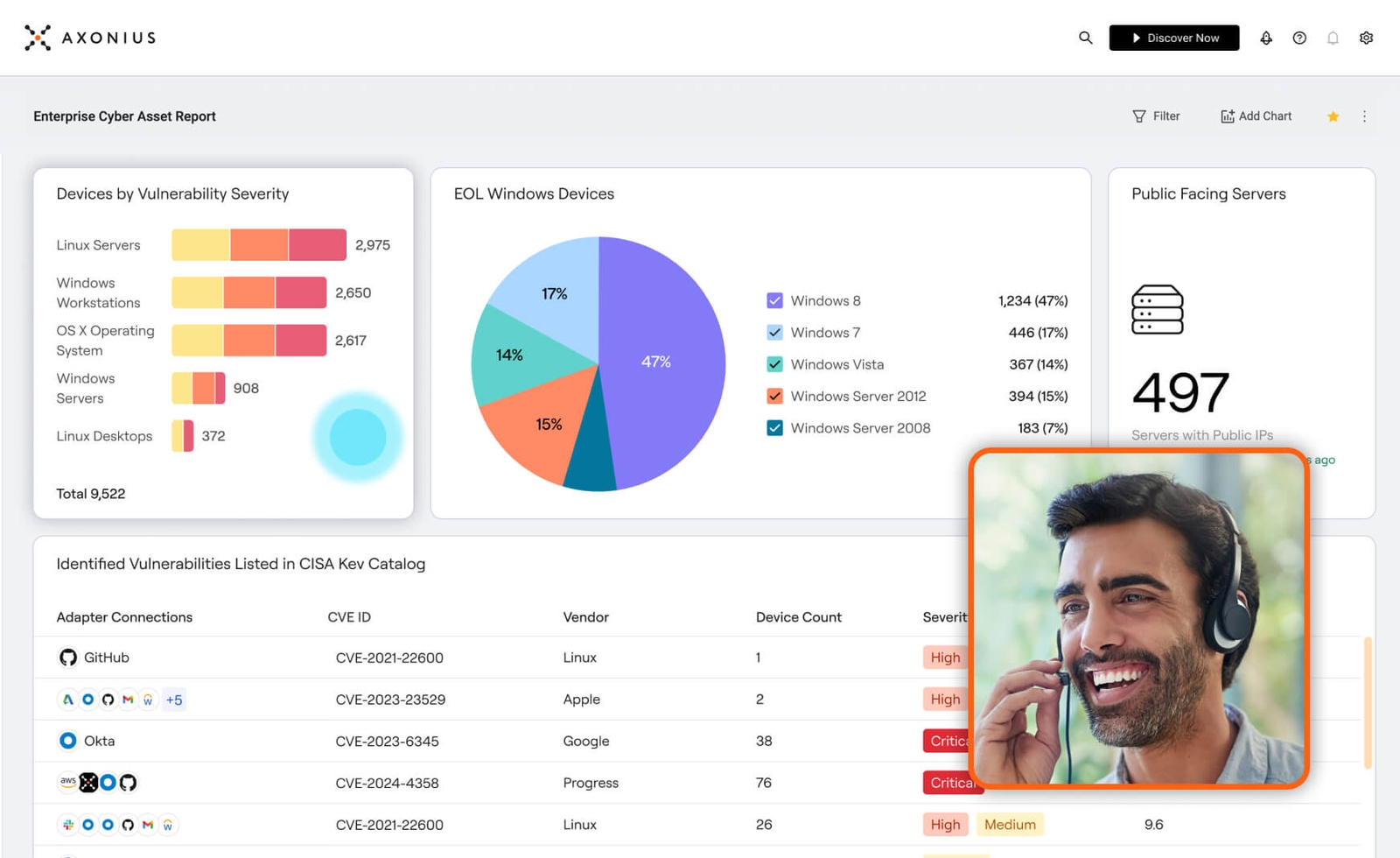
Aggregate vulnerabilities, exposures, and misconfigurations across all your IT and security tools into a single, unified view. Axonius eliminates silos to deliver a comprehensive risk picture, making it easy to uncover hidden gaps and take meaningful action.
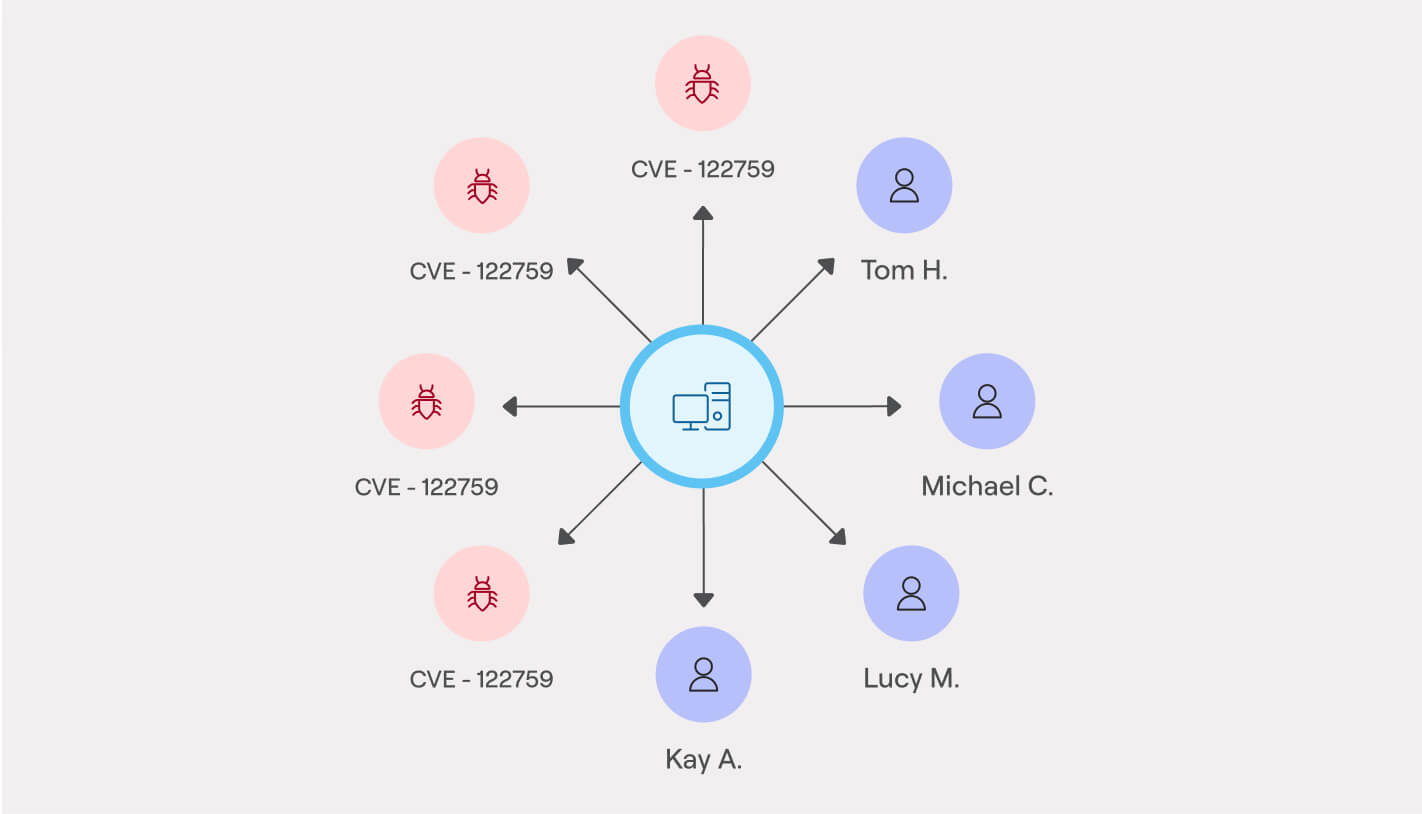
See risks in full context to act smarter
Visualize the connections between vulnerable software, devices, identities, and infrastructure to understand the scope and impact of risks. Axonius integrates data across systems to prioritize what matters most and drive targeted remediation.

Right-size prioritization to your capacity
Generate universal risk scores for assets and findings based on exposure, business impact, and exploitability. Axonius ensures teams focus on the highest-impact issues while aligning risk priorities with organizational goals.
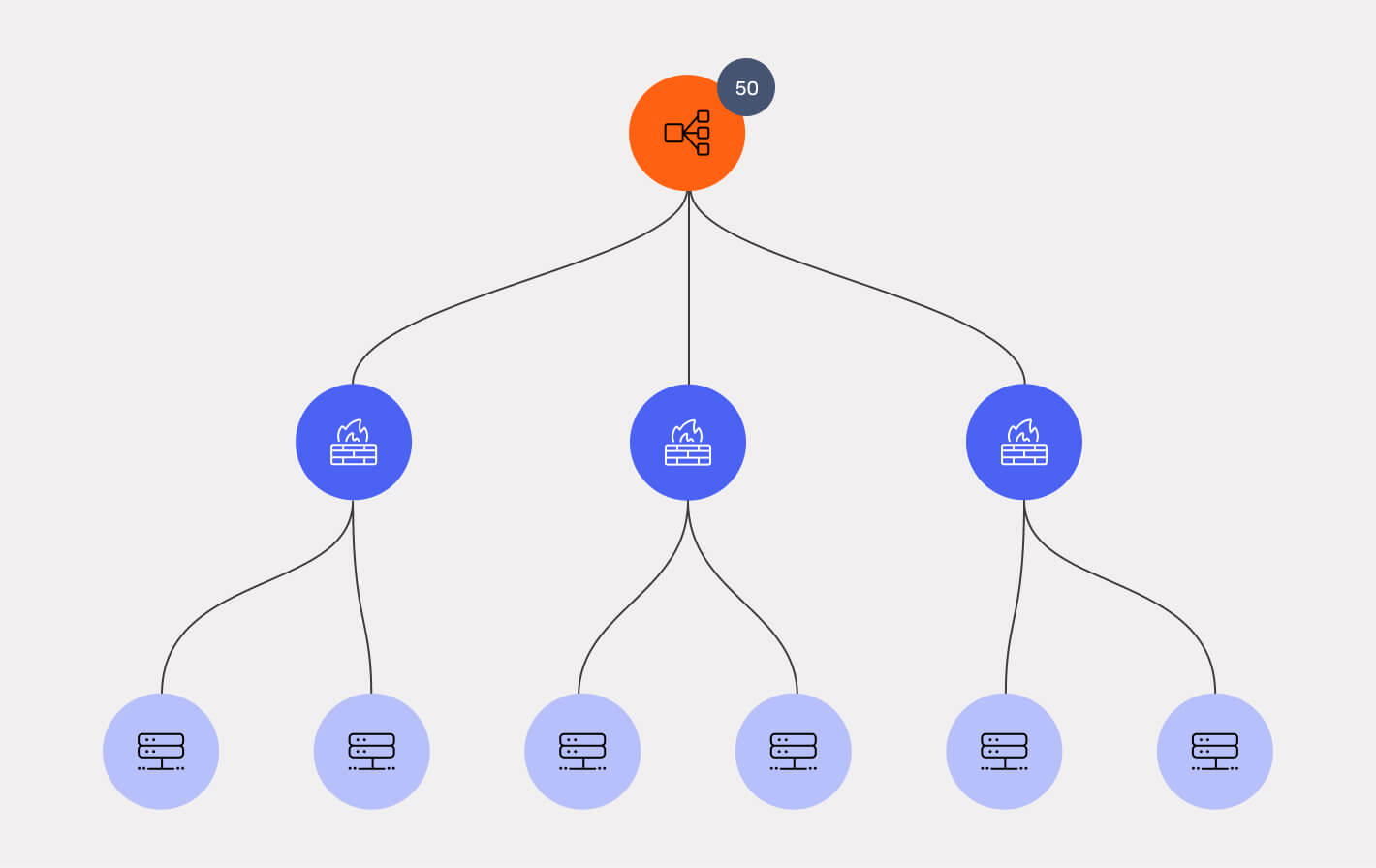
See exposure from the outside in and inside out
Identify vulnerable assets reachable through your load balancers, firewalls, and subnet configurations. Our configuration-based approach finds public routes of attack before any network traffic.
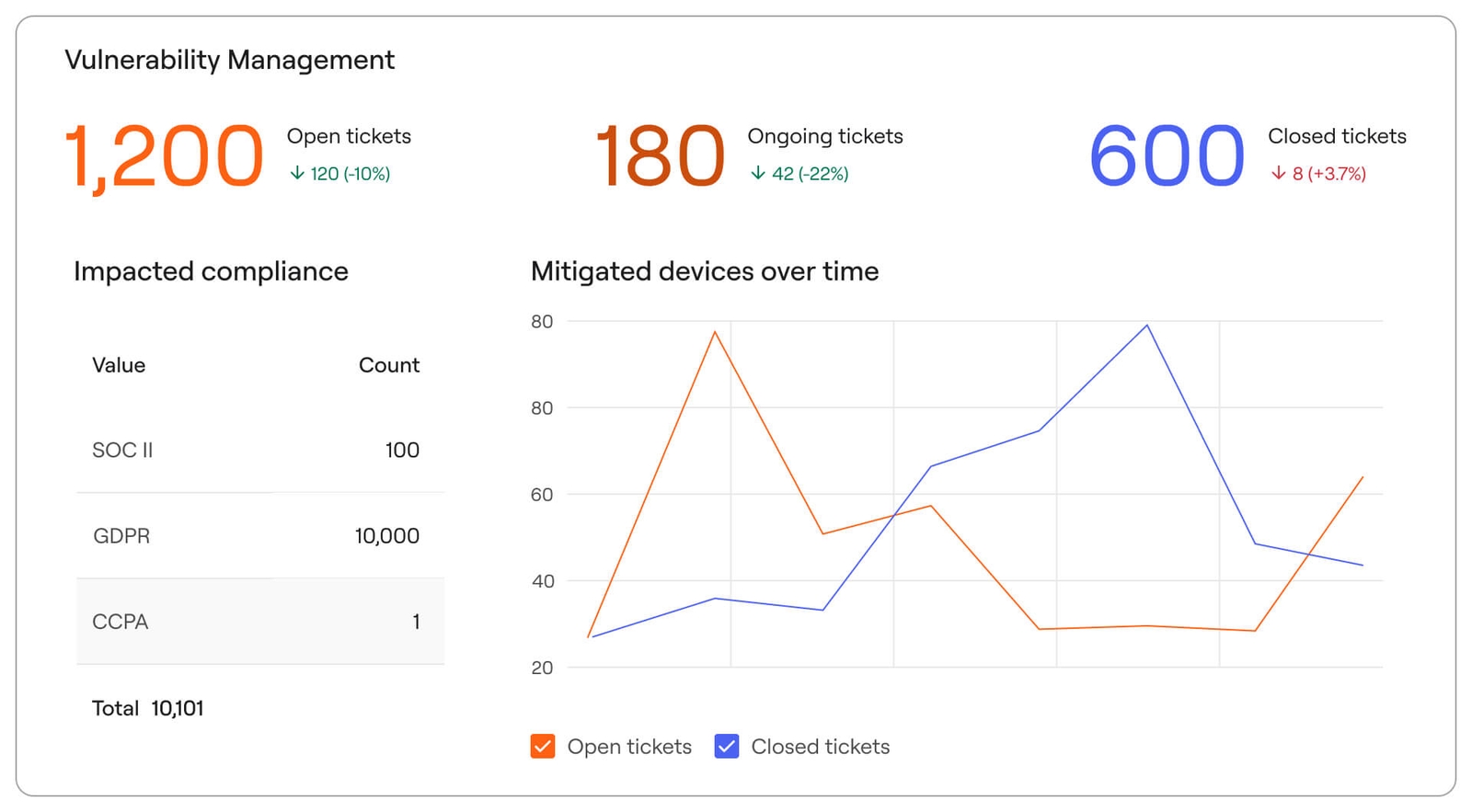
Close the loop on remediation efforts
Centralize the entire remediation process—from planning to tracking to auditing—in one platform. Axonius integrates seamlessly with existing workflows to ensure every step is streamlined and accountable.
Ready to take action against all types of exposures?
Schedule a personalized demo with an Axonius specialist.
The power to prevent exposures from becoming issues

Comprehensive risk clarity
Forget silos and partial visibility. Axonius unifies vulnerabilities, exposures, and misconfigurations into one platform, providing a holistic and actionable view of your total risk landscape.

Risk context that matters
You won’t get stuck with missing intel. Axonius enriches every risk with business context, mapping relationships between assets, identities, and infrastructure to help you act smarter.

More proactive actionability
Axonius uncovers exploitable paths and at-risk assets, empowering teams to take preemptive action and shrink the attack surface before adversaries strike.

Designed for cross-functional programs
No more juggling tools and teams. Axonius centralizes planning, tracking, and auditing to streamline the entire remediation lifecycle and ensure accountability.
Customers of all kinds and sizes trust Axonius to manage exposures

The Axonius Asset Cloud
Axonius is where posture, management, and operations converge across your core cybersecurity programs – all backed by our market leading asset intelligence.
See Axonius in action
Discover what’s achievable with a product demo, or talk to an Axonius representative.



.png?width=950&auto=webp&format=jpg&disable=upscale)



















